| [1]Xie Y, Yang D, He Q, et al. Zebrafish as a model system to study the physiological function of telomeric protein TPP1. PLoS One. 2011;6(2):e16440. [2]Takai KK, Hooper S, Blackwood S, et al. In vivo stoichiometry of shelterin components. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(2):1457-1467. [3]Takai KK, Kibe T, Donigian JR, et al. Telomere Protection by TPP1/POT1 Requires Tethering to TIN2. Molecular Cell. 2011;4 4: 647-659.[4]Abreu E, Aritonovska E, Reichenbach P, et al. TIN2-tethered TPP1 recruits human telomerase to telomeres in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30:2971-2982.[5]Lundblad V. Taking the measuree. Nature. 2003;423:926-927.[6]Blasco MA. Mammalian telomeres and telomerase:why they matter for cancer and aging. Eur J Cell Biol. 2003;82:441-446.[7]Giannone RJ, McDonald HW, Hurst GB, et al. The Protein Network Surrounding the Human Telomere Repeat Binding Factors TRF1, TRF2, and POT1. PLoS ONE. 2010;5(8): e12407.[8]Miller AS, Balakrishnan L, Buncher NA, et al. Telomere proteins POT1, TRF1 and TRF2 augment long-patch base excision repair in vitro. Cell Cycle. 2012;11(5):998-1007.[9]Choi KH, Farrell AS, Lakamp AS, et al. Characterization of the DNA binding specificity of Shelterin complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39(21):9206-9223.[10]Martínez P, Blasco MA. Role of shelterin in cancer and aging. Aging Cell. 2010;9:653-666.[11]Opresko PL, Kobbe Cv, Laine JP, et al. Telomere-binding Protein TRF2 Binds to and Stimulates the Werner and Bloom Syndrome Helicases. J Biol Chem. 2000;277(43):41110- 41119.[12]Chiang YJ, Hsiao SJ, Yver D, et al. Tankyrase 1 and Tankyrase 2 Are Essential but Redundant for Mouse Embryonic Development. PLoS ONE. 2008;3(7): e2639.[13]Ha GH, Kim HS, Go H, et al. Tankyrase-1 function at telomeres and during mitosis is regulated by Polo-like kinase-1-mediated phosphorylation. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19(2):321-332.[14]Donigian JR, de Lange T. The role of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase tankyrase1 in telomere length control by the TRF1 component of the shelterin complex. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:22662-22667.[15]Chang P, Coughlin M, Mitchison TJ. Tankyrase-1 polymerization of poly(ADP-ribose) is required for spindle structure and function. Nat Cell Biol. 2005;7:1133-1139.[16]Gelmini S, Poggesi M, Distante V, et al. Tankyrase, a positive regulator of telomere elongation, is overexpressed in human breast cancer. Cancer Lett.2004;216:81-87.[17]Flynn RL, Centore RC, O’Sullivan RJ, et al. TERRA and hnRNPA1 orchestrate an RPA-to-POT1 switch on telomeric single-stranded DNA. Nature. 2011;471:532-536.[18]Krüger AC, Raarup MK, Nielsen MM, et al. Interaction of hnRNP A1 with telomere DNA G-quadruplex structures studied at the single molecule level. Eur Biophys J. 2010; 39(9):1343-1350.[19]Choi YH, Lim JK, Jeong MW, et al. HnRNP A1 phosphorylated by VRK1 stimulates telomerase and its binding to telomeric DNA sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(17):8499-8518[20]Ford LP, Wright WE, Shay JW. A model for heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins in telomere and telomerase regulation. Oncogene. 2002;21(4):580-583.[21]Cairney CJ, Keith WN. Telomerase redefined: integrated regulation of hTR and hTERT for telomere maintenance and telomerase activity. Biochimie. 2008;90(1):13-23. [22]Brault ME, Autexier C. Telomeric recombination induced by dysfunctional telomeres. Mol Biol Cell. 2011;22(2): 179-188.[23]Ting NS, Pohorelic B, Yu Y, et al. The human telomerase RNA component, hTR, activates the DNA-dependent protein kinase to phosphorylate heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37(18): 6105-6115.[24]Fakhoury J, Marie-Egyptienne DT, Londoño-Vallejo JA, et al. Telomeric function of mammalian telomerases at short telomeres. J Cell Sci. 2010;123:1693-1704.[25]Sexton AN, Youmans DT, Collins K. Specificity Requirements for Human Telomere Protein Interaction with Telomerase Holoenzyme. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(41):34455-34464.[26]Cairney CJ, Keith WN. Telomerase redefined: integrated regulation of hTR and hTERT for telomere maintenance and telomerase activity. Biochimie. 2008;90(1):13-23. [27]Itahana K, Dimri G, Campisi J. Regulation of cellular senescence by P53. Eur J Biochem. 2001;268:2784-2791.[28]Feng Z, Lin M, Wu R. The Regulation of Aging and Longevity A New and Complex Role of p53. Genes Cancer. 2011; 2(4): 443-452.[29]Harly CB, Futcher AB, Greider CW. Telomeres shorten during aging of human fibroblasts. Nature. 1990;345:4458-4604.[30]Smogorzewska A , de-Lange T. Regulation of telomerase by telomeric proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73: 177-208.[31]Martínez P, Blasco MA. Telomeric and extra-telomeric roles for telomerase and the telomere-binding proteins. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11(3):161-176.[32]van Steensel B, de Lange T. Control of telomere length by the human telomeric protein TRF1. Nature. 1997;385(6618): 740-743.[33]Lee TH, Tun-Kyi A, Shi R, et al. Essential role of Pin1 in regulation of TRF1 stability and telomere maintenance. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(1): 97-105. [34]Sfeir A, Kosiyatrakul ST, Hockemeyer D, et al. Mammalian telomeres resemble fragile sites and require TRF1 for efficient replication. Cell. 2009;138:90-103.[35]Smith S, Giriat I, Schmitt A, et al. Tankyrase, a poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase at human telomeres. Science. 1998;282:1484-1487.[36]Smith S, de Lange T. Tankyrase promotes telomere elongation in human cells. Curr Biol. 2000;10:1299-1302.[37]Loayza D, De Lange T. POT1 as a terminal transducer of TRF1 telomere length control. Nature. 2003;423:1013-1018.[38]Nandakumar J, Podell ER, Cech TR. How telomeric protein POT1 avoids RNA to achieve specificity for single-stranded DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(2):651-656.[39]Palm W, Hockemeyer D, Kibe T, et al. Functional dissection of human and mouse POT1 proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29: 471-482.[40]Zhang DY, Wang HJ, Tan YZ. Wnt/β-catenin signaling induces the aging of mesenchymal stem cells through the DNA damage response and the p53/p21 pathway. PLoS One. 2011; 6(6):e21397. [41]Demidenko ZN, Korotchkina LG, Gudkov AV, et al. Paradoxical suppression of cellular senescence by p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:9660-9664.[42]Itahana K, Dimri G, Campisi J. Regulation of cellular senescence by P53. Eur J Biochem. 2001;268:2784-2791. |
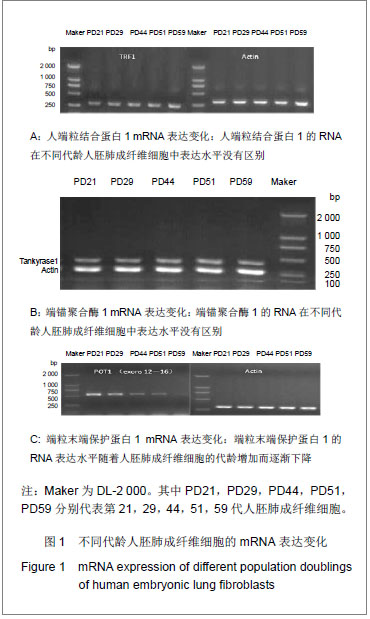

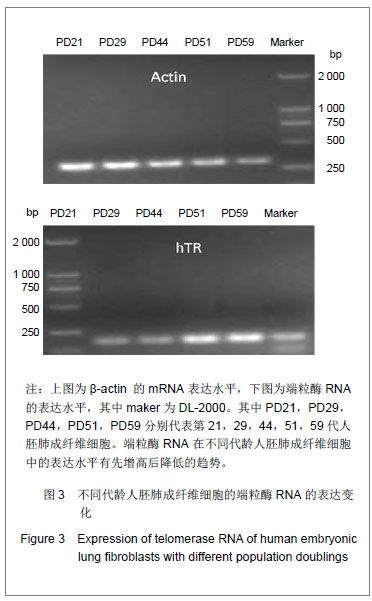

.jpg)